Nitriding-related Keywords:
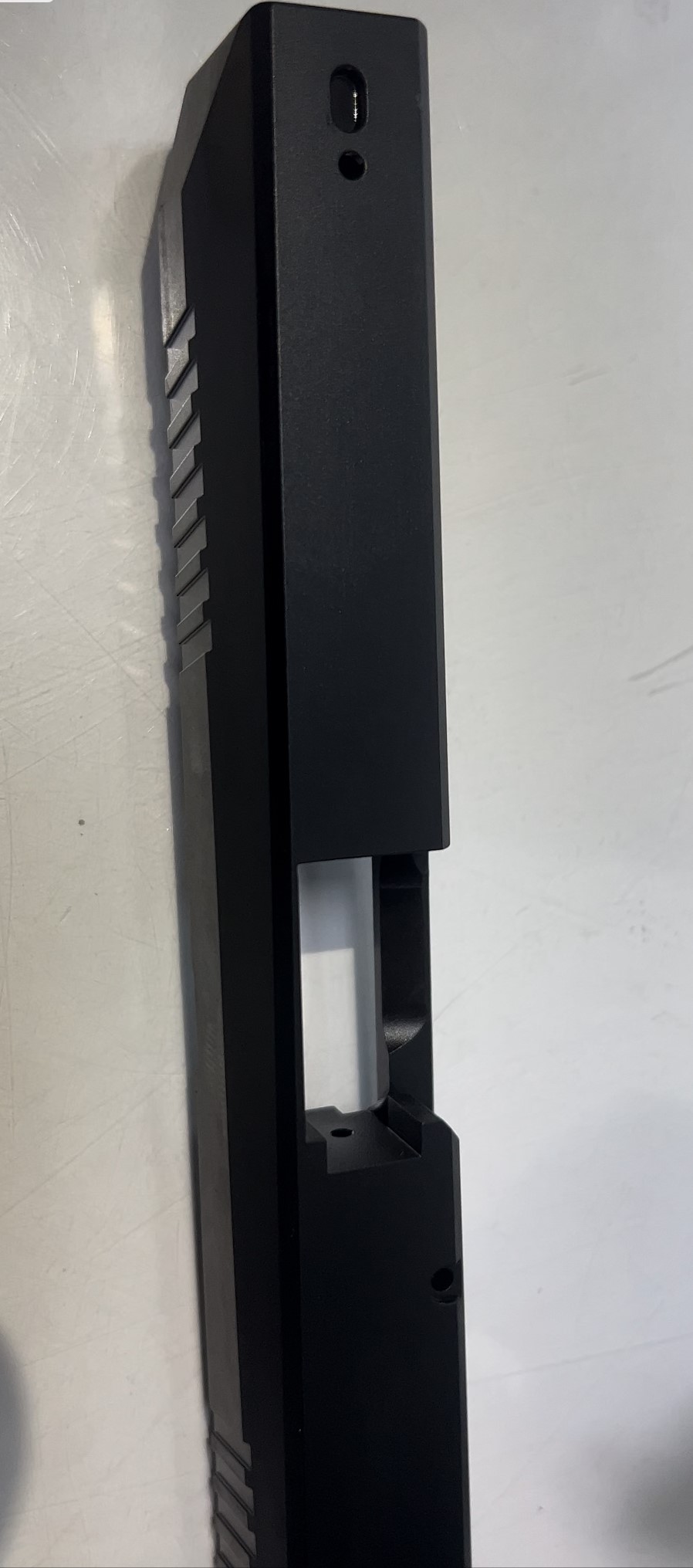
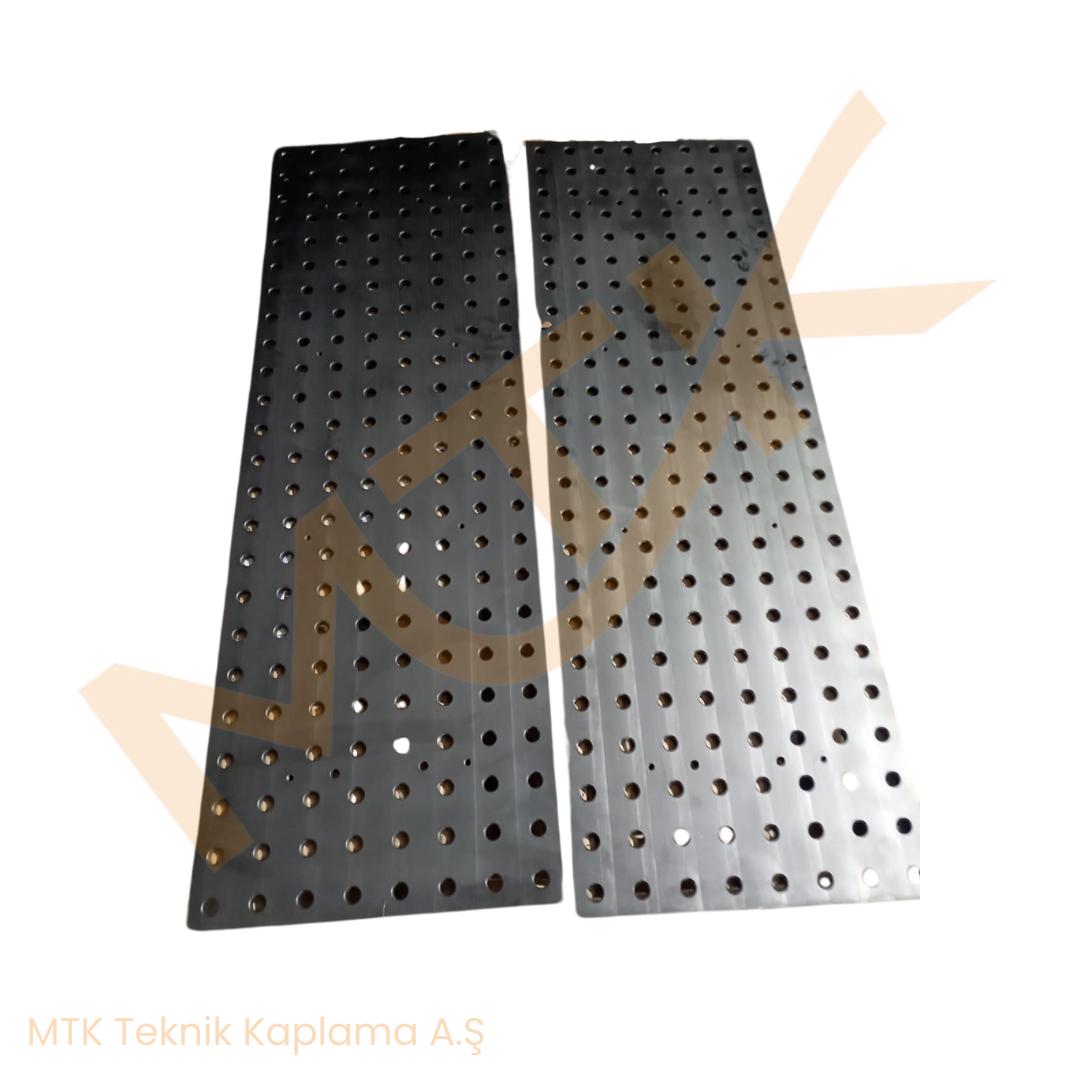
Liquid Nitriding (Salt Bath Nitrocarburizing) is a thermochemical process used to enhance the hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of metal surfaces. In this technique, metal parts are immersed in a molten salt bath that contains nitrogen and carbon-bearing compounds. The elevated bath temperature facilitates the diffusion of nitrogen and carbon atoms into the metal’s surface, creating a hardened, durable outer layer.
Key Features:
- Faster Processing: Liquid nitriding offers a quicker turnaround compared to gas nitriding due to the high heat transfer efficiency in the salt bath.
- Uniform Hardness: The process ensures a consistent case depth and surface hardness across the entire treated surface, which minimizes distortions.
- Corrosion Resistance: Often combined with post-oxidation steps (as in the QPQ process), the treated surface gains not only increased hardness but also a black oxide finish that enhances corrosion protection.
- Applications: It is widely used in automotive, tooling, and oil & gas industries to improve part longevity and resistance under stress.
The OPO process (Quench-Polish-Quench) is often paired with liquid nitriding to further refine the surface and add an aesthetically pleasing black oxide coating.
This technique is preferred for parts that require high fatigue strength and protection against both wear and corrosion. Industries such as defense and machinery benefit significantly from this treatment, particularly for components like gears, shafts, and tools




Yorumlar